Metal products frequently deteriorate over time due to exposure to harsh elements like high temperatures, oxygen, and wear. However, metal polishing can effectively prevent oxidation and contamination, resulting in a high-quality surface.
Polishing metal surfaces demands a certain degree of creativity. This article explores the benefits of metal polishing, outlines the steps involved, and describes various types of polishing finishes. Additionally, you will find useful tips for achieving successful metal plate polishing. Let’s dive in!
Benefits of Metal Polishing
Metal polishing offers numerous advantages during metal fabrication, enhancing shapes, designs, and features. This section will cover some of the common benefits of metal plate polishing.
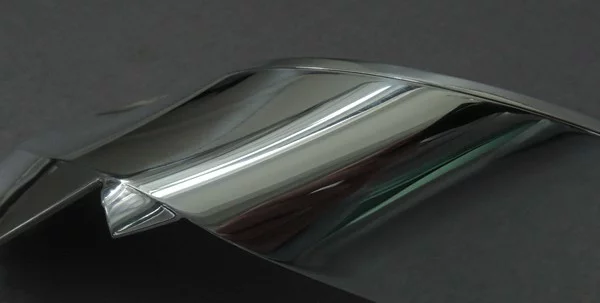
- Enhanced Product Aesthetics
Machined metal parts typically do not possess the smooth and appealing surface seen in finished products. The abrasive wheels of a polishing machine smooth out the rough surfaces of machined components, removing scratches, imperfections, tarnishes, and nicks to ensure a glossy and smooth finish. However, the desired aesthetic specifications can influence the processing time and cost of polishing metal parts.
- Protective Layer
Metal polishing, such as titanium polishing, offers significant benefits beyond surface quality enhancement. Polished metals not only look better for longer but also perform better than unpolished metals. The abrasive process of polishing helps resist contamination and oxidation, creating a protective layer that reduces wear, tear, and corrosion.
- Improved Light Reflection
Polished metal surfaces shine more brightly and vibrantly, resulting in effective light reflection. This property is particularly beneficial in applications requiring high reflectivity, such as architectural elements, jewelry, and decorative items.
- Enhanced Functionality
Metal polishing improves the functionality of metal components in specific applications, including precision instruments and machinery parts. By eliminating surface imperfections, polishing achieves a smooth and even finish, reducing friction and enhancing overall performance and conductivity.
- Increased Cleanliness
Polishing techniques provide metal parts with a finish that reduces the risk of bacteria and germs, which can damage and degrade surfaces. Properly polished metal components are easier to clean and maintain due to their smooth surfaces, reducing the time and effort required for cleaning. Additionally, polished surfaces require fewer harmful chemicals for cleaning, which can otherwise accelerate wear and corrosion.

Different Metal Polishing Techniques
Product engineers often employ various polishing techniques to improve the surface quality of their metal products. Before delving into the different methods of metal polishing, it’s essential to understand the pre-polishing procedures.
Surface Preparation Before Polishing
Properly preparing the metal surface before polishing is crucial. Here are the steps to ensure optimal surface preparation:
- Remove Rust or Corrosion: Eliminate any rust or corrosion present on the metal surface.
- Clean the Surface: Use a suitable cleaning agent, such as a mild detergent, to remove grease, debris, or other contaminants from the metal surface.
- Smooth Out Imperfections: Address all dents, scratches, and other imperfections on the metal surface to ensure a smooth finish.
- Rinse and Dry: After removing imperfections, rinse off any cleaning agents, abrasives, or rust removal residues. Thoroughly wipe and dry the surface to prevent water spots and further corrosion.
With the metal surface properly prepared, we can now explore the various metal polishing techniques through a step-by-step guide.

1. Hand Polishing Technique
Hand polishing is a manual method that utilizes various polishing compounds and tools. This technique involves direct contact between the polisher and the metal surface. Although it is more time-consuming than machine polishing, hand polishing offers personalized, controlled, and precise results. Here are the steps involved in the hand-polishing process:
- Select and Apply the Polishing Compound: Choose an appropriate polishing compound based on the type of metal and the desired finish. Common polishing compounds include jeweler’s rouge, metal polishes, and rubbing compounds. Apply the selected compound to the metal surface.
- Start Polishing: Using a moderate amount of pressure, rub the metal surface with the polishing compound in a circular or back-and-forth motion. Continue polishing until you achieve the desired level of shine. You may need to reapply the compound as necessary to maintain effectiveness.
- Clean and Inspect: Once the desired polish is achieved, use a soft cloth to clean the metal surface, removing any residue from the polishing compound. Inspect the surface for any remaining imperfections or areas that may require additional polishing.

2. Machine Polishing Technique
The machine polishing technique employs power tools such as dual-action or rotary polishers. This method is suitable for metals like titanium, nickel, chrome, bronze, stainless steel, and copper. It is commonly used by manufacturers in industries such as electronics, aerospace, and medical devices to achieve desired results.
Here is a step-by-step guide for the machine polishing technique:
- Choose the Right Polishing Pad: Select the appropriate polishing pad based on the required level of polishing. Options include wool, foam, or microfiber pads, each with varying levels of aggressiveness.
- Apply the Polishing Compound: Apply a small amount of polishing compound to the polishing pad, ensuring an even coat without overloading the metal surface.
- Program the Speed and Begin Polishing: Set the machine polisher to the desired speed. Begin polishing by moving the machine in a slow, overlapping motion across the surface of the metal parts. Apply moderate pressure and avoid staying in one spot for too long to prevent heat buildup.
- Check the Progress: Periodically stop to inspect the progress. Wipe off excess polishing compound and check for any defects. Replace the polishing pad if necessary and adjust the polishing pressure and speed as needed.
- Complete the Polishing: Once you have achieved the desired level of shine, use a soft cloth to clean the metal surface, removing any remaining residue.

3. Chemical Polishing Technique
Chemical polishing involves the use of specialized chemical compounds to remove thin layers from the metal surface, resulting in an improved and aesthetically appealing finish. This technique is particularly suitable for delicate parts. Here is a detailed breakdown of the chemical polishing process:
- Select a Suitable Chemical Polishing Solution: Choose the appropriate chemical solution based on the type of metal. These solutions typically contain etchants, which selectively dissolve the surface layer of the metal.
- Prepare the Solution: Follow the provided instructions to mix the chemical polishing solution correctly. This usually involves diluting the compound with a specific solvent or water.
- Submerge the Metal Object: Fully immerse the metal component in the chemical polishing solution, ensuring the solution covers the entire surface area intended for polishing.
- Monitor the Chemical Process: Carefully observe the reaction between the metal and the polishing solution. The duration required for polishing depends on the type of metal and the desired outcome. Due to the delicate nature of this process, close monitoring is essential.
- Rinse and Dry: After removing the metal parts from the solution, rinse them thoroughly with water. Dry the parts completely to prevent water spots or corrosion.

Types of Metal Polishing Finishes
Different types of polishing finishes are suitable for various metal products. Let’s explore the details:
- Mirror Finish
A mirror or high-polish finish offers high reflectivity, making it ideal for stainless steel products. This finish is excellent for concealing welded metal components and allows for easy cleaning. Achieving a mirror finish requires careful polishing and buffing techniques, resulting in a reflective, smooth, and flawless surface, akin to a mirror.
- Brushed Finish
A brushed finish creates an aesthetic pattern of delicate parallel lines. This finish is perfect for parts intended for both outdoor and indoor applications, where they are exposed to sunlight or bright indoor lighting. Many kitchen appliances feature a brushed finish. To ensure uniform lines, a high-grade abrasive is necessary.
- Satin Finish
The satin finish is a common metal polishing type that provides a toned-down, low-gloss appearance. Using fine abrasives, you can polish metal parts to achieve an even surface with a slight sheen. This finish gives the metal a smooth touch and a subtle elegance, making it suitable for applications requiring a refined appearance, such as jewelry, household appliances, and architectural elements.
- Antique Finish
An antique finish enhances the appearance of metal by giving it an aged or eroded look. This finish is often used for furniture, architectural elements, and decorative items, imparting a sense of history and character. Achieving an antique finish can involve manual distressing techniques, patination, and chemical treatments to create various effects like discoloration, tarnishing, or a worn-out appearance. The primary goal is to mimic the natural aging process, giving the metal a lasting, antique appeal.

Tips for Optimal Results in Metal Polishing
Here are some helpful tips to ensure successful metal polishing:
- Choose the Appropriate Polishing Tools
- Use fast-cutting pastes and avoid rubbing a spot for too long to prevent overheating the metal surface.
- For roughing, use abrasive discs with polyester films to achieve uniform roughness levels.
- Apply a reliable wax polish to preserve an already polished metal surface.
- Ensure your abrasive material is neither too liquid nor too hard.
- Apply Polishing Compounds Discretely
- Vary the polishing direction constantly to ensure uniformity, especially for components with irregular shapes and sizes. Avoid polishing metal parts in a unidirectional manner.
- Apply polish across marks and scratches on metal surfaces rather than along them to achieve better results.
- Take Necessary Safety Precautions
- Wear appropriate safety gear during polishing operations, as the process can be hazardous without proper protection.
- Eliminate grease and other contaminants from the work area to maintain a safe and efficient polishing environment.

Conclusion
Metal polishing enhances the surface quality of metal products, providing them with superior aesthetic appeal, increased longevity, and improved functionality. This article has covered the benefits of metal polishing and offered insights on how to achieve the best results from this post-processing method.
For professional assistance with machining and polishing your metal projects, AS Prototypes is the right manufacturer to contact. We offer reliable CNC metal machining and surface finishing services. Trust us to deliver the desired polishing results for your custom metal parts. Reach out to us today, and let us handle your project!
FAQs
What tool can I use for polishing metal parts?
The buffing wheel is the standard tool for applying polishing compounds to the surface of metal components. You should apply the polishing compound to the buffing wheel while it spins, using either an industrial-scale motor polisher or a handheld rotary drill.
How is buffing different from polishing?
Polishing is a more delicate process that uses finer abrasive materials to achieve a shiny and reflective surface. In contrast, buffing is more intensive and involves using an abrasive compound to remove marks and scratches. The choice between these two methods depends on the desired result for your project.
What are the main reasons for polishing metal products?
Manufacturers polish metal products to prevent contamination risks, enhance surface appearance, achieve a reflective finish, and resist corrosion.

