What is Metal 3D Printing?
Metal 3D printing is a form of additive manufacturing that builds parts by melting and fusing metal particles layer by layer. This technique is frequently selected over traditional manufacturing methods like CNC machining or metal casting, as it not only yields parts with comparable strength and durability but also offers greater design flexibility. Metal 3D printing excels in creating intricate designs such as lattices and structures optimized through topology, which are typically unachievable with conventional CNC machining processes.
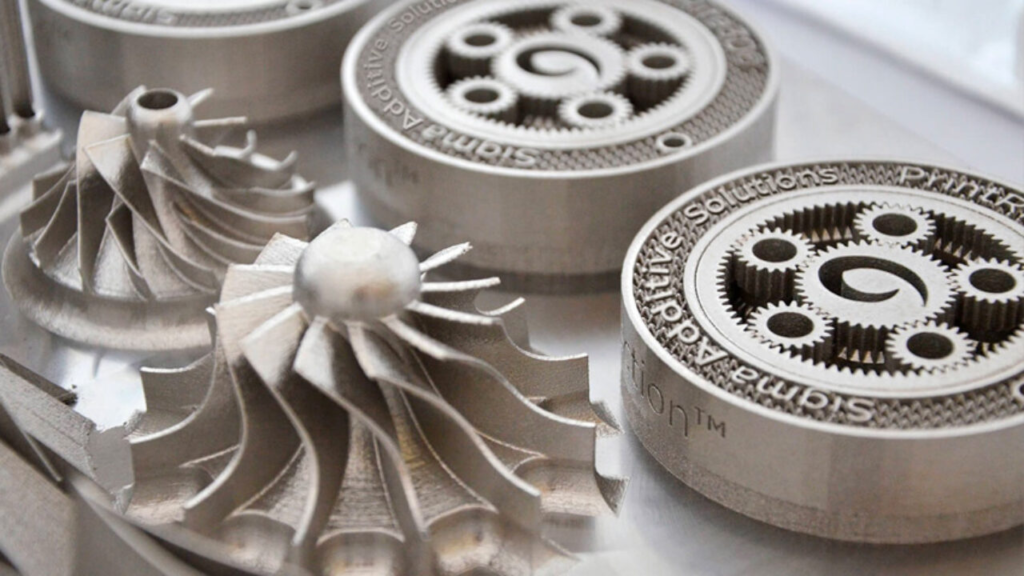

Advantages of Metal 3D Printing
Metal 3D printing offers several benefits, particularly in the production of complex, high-performance metal parts suitable for various applications. This technology enables the creation of parts with isotropic qualities, ensuring consistent strength across all directions. It leverages the robust mechanical properties of various metals, including aluminum, stainless steel, titanium, Inconel, tool steel, and composites of stainless steel and bronze.
One significant advantage of metal 3D printing is its ability to consolidate multiple components into a single, more robust structure. This integration reduces potential failure points that might arise from joints like threads and inserts.
Furthermore, metal 3D printing streamlines the manufacturing process by allowing direct transmission of CAD designs to the printer, which can be more cost-effective and faster compared to traditional machining. Traditional methods often involve additional costs for tooling and extended machining times. In contrast, metal 3D printed parts can generally be produced in less than a week, offering a quicker turnaround.
Choosing Between DMLS or Binder Jet Metal
AS Prototypes offers metal 3D printing services that feature two primary technologies: Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) and Metal Binder Jetting. Both methods are adept at producing metal prototypes, tooling, and on-demand production parts. However, they differ in the types of metals they utilize, their fusing techniques, and the mechanical properties of the finished parts. These differences also extend to varying costs and production lead times associated with each method.
Overview of Direct Metal Laser Sintering
Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), sometimes referred to as Selective Laser Melting (SLM), employs a high-precision laser to fuse fine metallic powder layer by layer, starting from the base. This process is particularly beneficial for creating fully dense parts, making it ideal for applications involving fluid transfer. DMLS is compatible with a variety of metals including aluminum AlSi10Mg, stainless steel, maraging steel, tool steel, cobalt chrome, and Inconel. While DMLS tends to be more costly compared to binder jetting, it offers enhanced mechanical properties that are crucial for high-precision applications.
Direct Metal Laser Sintering Material Properties
Aluminum AlSi10Mg
Stainless Steel 17-4
Stainless Steel 316/L

Overview of Binder Jet 3D Printing
Metal binder jetting is a layered additive manufacturing process that begins by selectively applying a binding agent to a bed of metal powder, shaping it into a three-dimensional form. This formed part is then allowed to cure before being sintered or infiltrated with bronze in a furnace. The support for any overhanging features during this process comes from the surrounding loose powder, which typically negates the need for additional post-processing.
The binder jetting technique is favored in metal 3D printing for its cost-effectiveness and speed, making it suitable for high-volume production. It produces parts that are approximately 95% dense or more, making them viable for functional prototypes and final-use components. Additionally, metal binder jetting is popular among artists and hobbyists for its ability to construct complex geometries at a lower cost compared to DMLS or traditional machining.
However, parts produced via binder jetting are susceptible to shrinkage. To accommodate this, engineers should incorporate design-for-manufacturing principles, such as adjusting the CAD model size by 1-2% and enlarging holes to compensate for dimensional changes during the sintering process.
Metal Binder Jetting Material Properties
X1 Metal 420i (420 stainless infiltrated with bronze)
Six finishes available

Applications of Metal 3D Printing in Various Industries
Metal 3D printing serves a wide range of applications across various industries due to its ability to rapidly produce tools and components with intricate designs. In industrial settings, this technology is particularly useful for creating parts that feature complex curvatures and thin walls, such as conformal jigs, fixtures, stamps, dies, and cutting inserts.
In sectors like consumer products, robotics, aerospace, and defense, metal 3D printing is employed to fabricate items with integrated fastening features, end-effectors, and intricate metal lattice structures. The robust durability and strength of metal 3D printed parts make them ideal for use in fully functional late-stage prototypes or as final-use components in any of these fields.