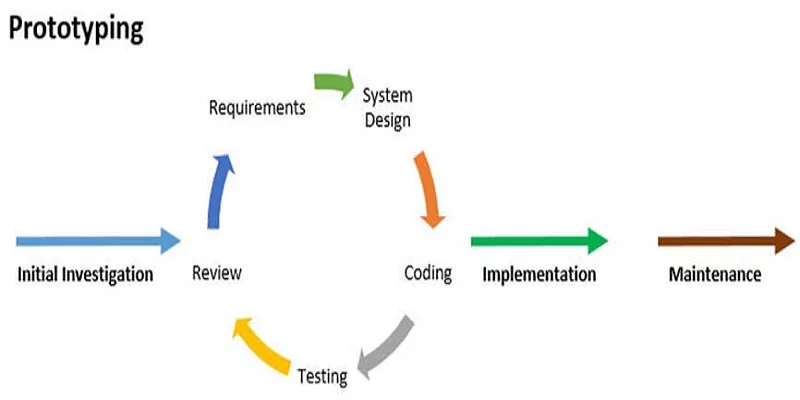
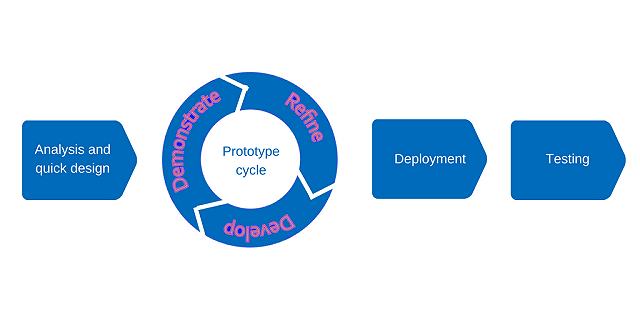
The product development process typically begins with the design phase and progresses to prototype development. Creating a prototype is a crucial step in developing new products or technologies, serving as a tangible representation of the conceptual design used to illustrate and validate various aspects.
Prototypes can range from simple handmade models to fully operational representations that demonstrate how the design will function in real-world conditions. Advancements in rapid prototyping have made it easier for manufacturers to create prototypes quickly, allowing for efficient design verification. These prototypes not only help refine the product but also play a vital role in convincing customers and expanding the product’s market potential.
The Impact of Rapid Prototyping Techniques in Industry
Rapid prototyping techniques are transforming industries by reducing costs and increasing efficiency. This set of methods allows for the quick creation of physical prototypes, making the development process easier, more accurate, and less time-consuming. Typically, prototypes are fabricated using 3D printing or other additive manufacturing technologies, utilizing CAD model data.
CNC machines are also employed to convert 3D models into physical representations. The key distinction between 3D printers and CNC machines lies in the materials and tools used for prototype development. Additionally, 3D printers require significantly less space compared to traditional subtractive methods like CNC milling, lathes, and precision grinding, making them a more favorable option for manufacturers.
The rise of user-friendly modeling software has further facilitated the adoption of rapid prototyping techniques, enabling both domestic and industrial users to easily create 3D models.
Common Technologies Used in Rapid Prototyping:
- 3D Printing (3DP)
- Shape Deposition Manufacturing (SDM) and Mold SDM
- Solid Ground Curing (SGC)
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
- Selective Laser Melting (SLM)
- Stereolithography (SLA)
- CNC Machining
- Ballistic Particle Manufacturing (BPM)
- Directed Light Fabrication (DLF)
- Direct-Shell Production Casting (DSPC)
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
- Laminated Object Manufacturing (LOM)
- Laminated Resin Printing (LRP)

Prototype Categories
Prototypes can be categorized based on the conceptual design and the final product being developed:
- Working Prototype
A working prototype closely represents nearly all features and functionalities of the final product, allowing for comprehensive testing and evaluation. - Visual Prototype
A visual prototype showcases the shape, dimensions, and appearance of the conceptual design but does not demonstrate its functionality. This type of prototype is typically easier to create than working prototypes. - User Experience Prototype
This prototype includes enough detail to assess user interaction and experience, serving as a tool for further research and feedback. - Functional Prototype
Similar to a working prototype, a functional prototype demonstrates key functionalities but may be created using different techniques or at a different scale than the final product.

Importance of the Prototype Development Process
The prototype development process is a crucial aspect of product development, offering insights into various factors that influence the final product. Here are some key benefits:
- Evaluation and Testing of Design
Creating a prototype allows for real-world evaluation of the design, enabling manufacturers to assess different components and identify which aspects need revision or removal. This hands-on testing helps ensure that the product performs effectively before entering production. - Determination of Production Costs and Issues
Developing a prototype before actual production provides a preview of the manufacturing process. This allows manufacturers to identify potential changes needed to streamline production and minimize costs. Additionally, any challenges in the production process can be addressed early, facilitating the selection of the most efficient and cost-effective production methods. - Sales and Customer Engagement
A prototype is more compelling to customers than a conceptual design, making it easier to sell the product. Demonstrating a tangible prototype allows manufacturers to gather customer feedback and make adjustments based on their preferences, which is not feasible once the product is fully developed. Engaging customers during the prototype phase enhances the likelihood of market success.
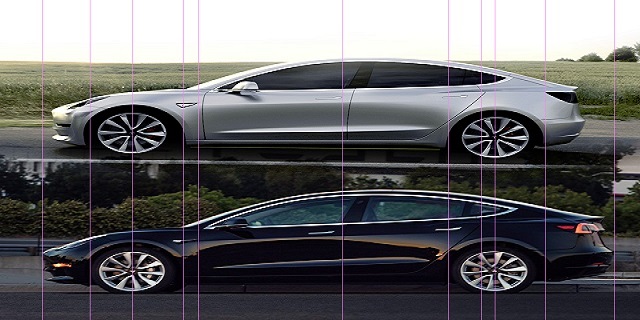
Difference Between Prototype and Actual Product
While engineers and developers strive to minimize differences between prototypes and actual products, several key distinctions often remain:
- Material Used
Prototypes are typically made from materials that are easier to fabricate and less expensive, yet possess similar properties to those of the final product. In some cases, the materials for the final product may not be available, leading to the use of alternative materials in the prototype. This difference can affect the appearance and finish of the final product compared to the prototype. - Manufacturing Process
Final products are usually produced in large quantities using mass production methods that are cost-effective and time-saving. These methods may not be applicable to prototypes, as the materials and fabrication techniques can differ. Consequently, prototypes are often created using simpler techniques, which can also impact their appearance. - Appearance and Finishing
Due to variations in materials and manufacturing processes, the aesthetic qualities of the prototype may differ from those of the final product. This includes aspects like surface finish, color, and overall visual appeal.
Concluding Remarks
The prototype development process is undeniably essential in the industry. Prototypes help identify and reduce errors in the conceptual design, preventing potential issues during product development. While differences may exist between prototypes and actual products, the primary purpose of prototypes is consistently met, facilitating the development process in numerous ways.
At AS Prototypes, we specialize in rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing of plastic and metal parts. We offer a comprehensive solution from prototype to production, enabling you to bring your product to market quickly and efficiently. If you’re seeking a reliable prototype manufacturer for your project, feel free to contact us.