Automotive development often requires small initial quantities for validation procedures, posing significant challenges for parts manufacturers. When clients request just a few dozen pieces, it can be difficult to accommodate, leading auto suppliers to frequently rely on custom machined solutions. Traditional, long-lasting standard tools are costly and generally impractical for small batch production that demands low volumes. Rapid prototyping companies, however, excel in understanding the needs of designers and offering customized aluminum machining services to meet the requirements of small quantities or even a single part.
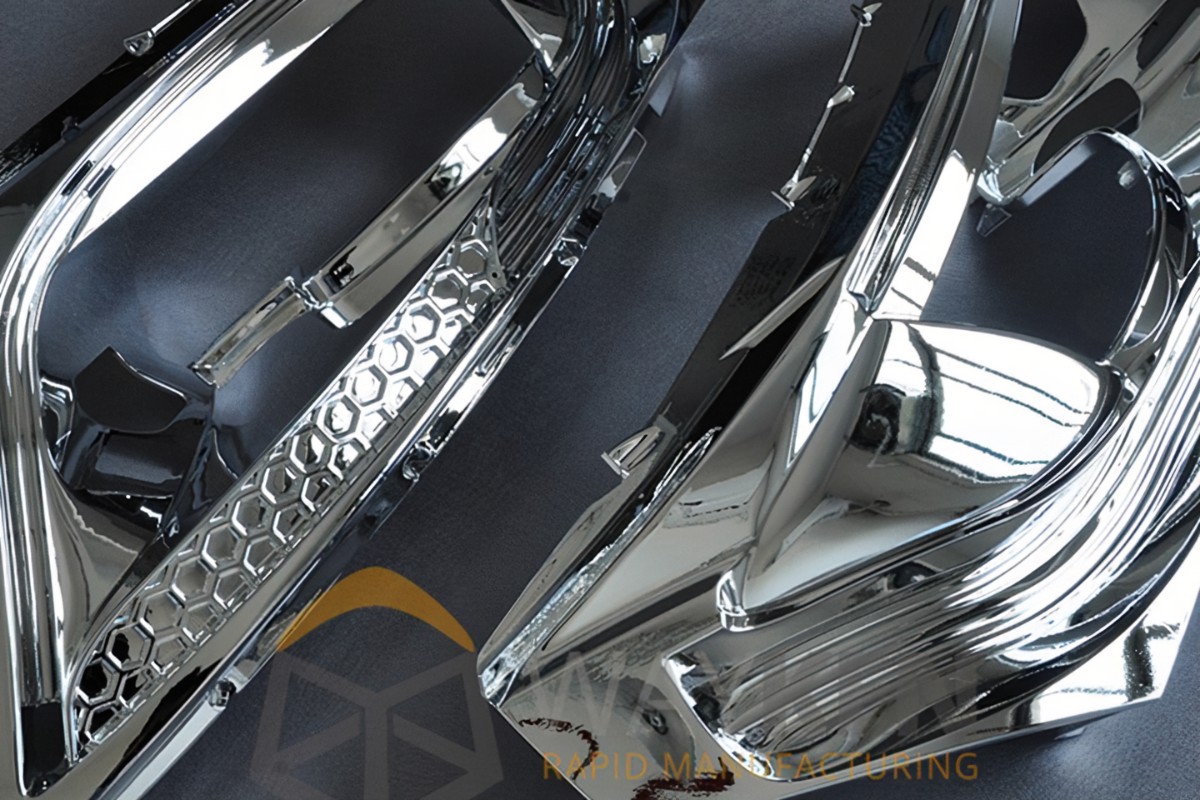
One of the most challenging tasks in rapid prototype projects, particularly in the lighting system, is creating the aluminum reflector. Only the most experienced prototype manufacturers can satisfy the stringent demands of optic designers. The reflector is a critical component of a headlamp, serving both an optical function and significantly influencing the lamp’s appearance. The captivating light from the headlights of BMW and Audi, as well as the taillights, owes much to the reflector. In high-end automotive prototyping, aluminum reflectors are essential, and product designers especially expect prototype manufacturers to fully understand and address all the intricate details they are concerned with.
1. What Is The Best Process To Produce An Aluminium Reflector Prototype?
For auto parts, rapid prototyping manufacturers often provide a range of processing options to cater to different needs. These options include 3D printing (additive manufacturing), urethane casting (using silicone molds), Reaction Injection Molding (RIM), and rapid tooling.
High-quality surface roughness is often required for these parts, typically needing to be lower than Ra 0.2 μm with a mirror gloss finish. Standard SLS and other rapid prototyping processes generally cannot meet these stringent surface quality requirements. Additionally, as a critical optical component, the accuracy of the part must be controlled within or below 0.05 mm. Therefore, CNC milling is the best option for machining aluminum reflectors. This method excels in producing parts with high precision and superior surface quality.
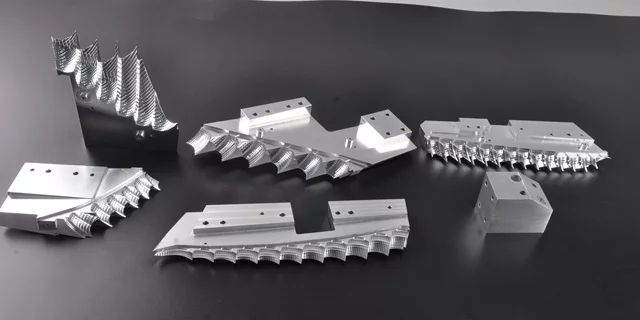
Due to the complex structure of the reflector, 5-axis CNC machining is necessary to complete the production. For certain assembly structures on the backside, auxiliary machining techniques such as Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) are also required to clear the corners effectively.
2. Choice Of Material
In the prototype production of automotive lighting parts, the most commonly used aluminum alloys are 2024, 5052, 6061, and 7075.
For parts like heatsinks, Al-6061-T6 is often chosen as the machining material due to its ease of processing. However, for components such as reflectors that require a mirror gloss surface, Al 7075-T6 is typically used. This alloy is widely utilized in the automotive and aerospace industries, including applications like aircraft wings and headlamp reflectors. Although the higher hardness of Al 7075-T6 means it requires more processing time, the advantage is that the final surface can achieve a mirror-like shine.
3. Machining Process
3.1 CNC milling
3.2 EDM
Due to the complex structure of the lamp, many details cannot be fully processed by even high-precision 5-axis CNC machines in a single operation. CNC programming engineers, who possess extensive experience in prototype lamp manufacturing, must analyze the feasibility of machining upon receiving the lamp design drawings. For reflectors, the critical optical surfaces are milled using CNC processes. However, the rear side of the reflector often features important assembly structures that are difficult to machine with CNC milling alone, as it tends to leave large radii on the corners.
To address this issue, technicians create copper electrodes and use Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) as an auxiliary process to clear the corners effectively. This additional process is time-consuming but necessary to achieve the required precision and detail.
3.3 Post finish
In the later stages of prototype production, processes such as deburring, polishing, plating, and other hand-finished post-processing work are particularly important, as they directly determine the final appearance of the part.
For reflectors that require a mirror gloss finish, there are two primary methods to achieve this:
- Manual Polishing: This method involves carefully polishing the surface to achieve a mirror-like gloss. However, special attention must be given to the optical surfaces, as some optics require sharp edges. The polishing process can potentially leave radii on these edges, which must be avoided to maintain the integrity of the design.
- Plating: In this method, the surface is first meticulously milled to ensure a smooth finish free of impurities. After this preparatory work, the reflector is plated to achieve a bright and beautiful final surface. This method can produce a highly reflective and aesthetically pleasing finish.
Both methods require precision and care to ensure that the final product meets the high standards of quality and appearance required for automotive lighting components.
Conclusion
At AS Prototypes, we specialize in providing customized aluminum machining services tailored to the stringent requirements of automotive lighting systems. Our expertise in CNC milling, EDM, and post-finish techniques ensures that we deliver high-quality aluminum reflectors with precision and superior surface quality. Whether you need small initial quantities for validation or a single part, AS Prototypes is your trusted partner for rapid prototyping solutions. Contact us today to learn how we can help bring your designs to life with unmatched accuracy and attention to detail.





