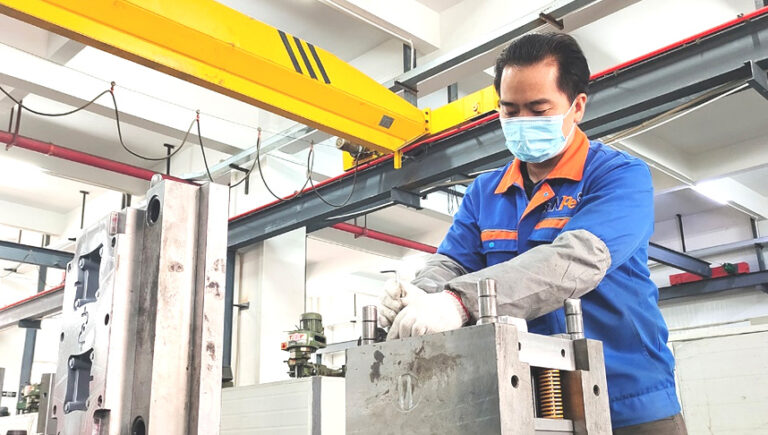
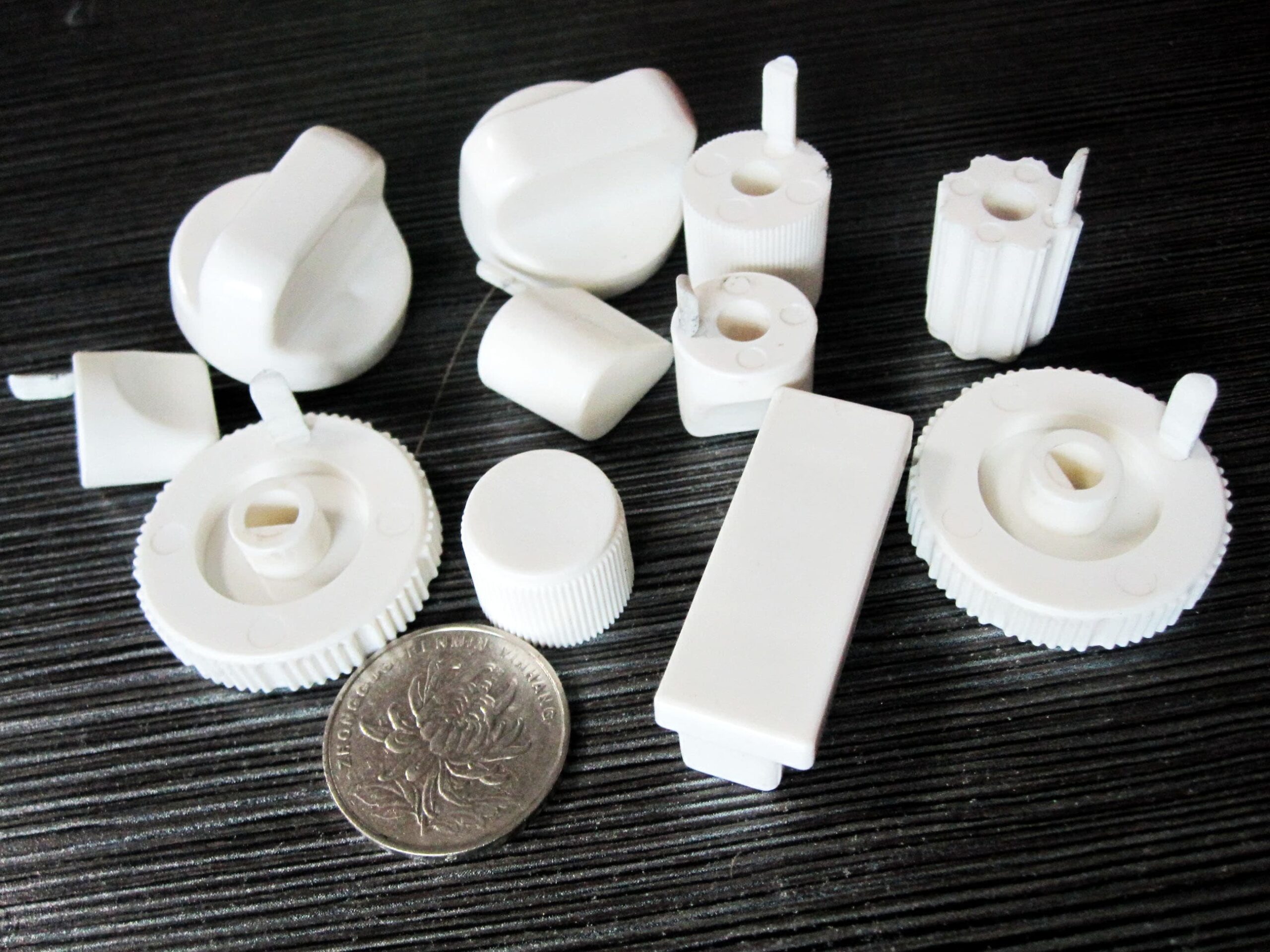
Many plastic manufacturers are dedicated to taking a proactive approach to meet the needs of our customers for the quick turnaround on molded plastic parts. Meanwhile, the advantages of low volume production play a great role in how to mold plastics. Acknowledging, production of low volume plastic molding parts needs using the different manufacturing procedures available. Short-run injection molding can be used in the production of real injection molded pieces depending on your specified amount of elements that can only be used as an earlier runoff.
Plastic Injection Molding
Low volume plastic molding, also known as low-volume injection molding, is a process that produces high-quality and precise parts quickly. It is the preferred method for manufacturing large quantities of finished plastic components for both industrial and commercial applications. In this process, melted resin is injected under high pressure into the chamber of a metal die, where it cools instantly to form a solid shape. Depending on the complexity and size of the part, a single cycle to create a complete piece can take anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes.
Low Volume Plastic Molding Process
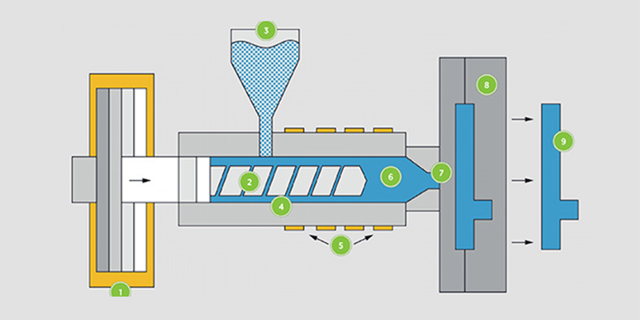
To begin the plastic injection molding process, it is essential to ensure all necessary tools are ready. Following each step meticulously is crucial for achieving an accurate finished product. Initially, plastic resin, which comes in the form of raw granules, is desiccated to attain the appropriate moisture levels. If needed, these granules can be mixed with color shades or masterbatch colors. Once dried, the granules are poured into the hopper of the injection molding machine.
Inside the machine’s container, an alternating screw moves the granules towards the mold. In the next step, the granules are mixed and heated within the barrel until they melt completely, forming a liquid resin. The mold, which is preheated, then closes automatically. The liquid resin is injected under high pressure through an opening into the mold chamber. Afterward, the mold is cooled to solidify the resin inside. Once the resin has hardened, the mold opens, and the finished piece is removed, allowing the process to begin anew.
Short Run Injection Molding
Prototype injection molding, also known as short-run injection molding, is used for producing injection-molded pieces in limited quantities, often for one-time run-offs. This process is ideal for creating operational prototypes, bridge tooling, and short production runs. It allows companies to produce small quantities of plastic parts based on specific quantity needs.
The short-run injection molding process begins with loading a 3D computer-aided design (CAD) file to quickly generate a mold. Once the design is uploaded, molding and processing can commence. Engineers then evaluate the models to ensure they meet the required specifications. Upon approval of the design by the engineers, the construction of the injection mold begins. After the mold is built, you will have the opportunity to examine a sample and provide approval. Once all these steps are completed, part production can begin.
Methods Of Low Volume Plastic Molding Parts
Three alternative technologies that can be utilized for producing low-volume plastic molding parts are pressure forming, structural foam molding, and reaction injection molding.
Pressure Forming
Commonly known as vacuum forming or thermoforming, this process involves draping a heated plastic sheet over a hollow or elongated mold. Initially, the plastic sheet is stretched, and then a vacuum is applied to the apparatus, followed by the application of pressure to the back of the sheet to conform it to the desired shape within the mold. Once the part is formed, any excess material is trimmed away using a CNC cutting machine.
Reaction Injection Molding
This type of rapid injection molding involves injecting a liquid thermoset material, which is mixed at low pressures. The resulting material is rigid and dense, with various types of reaction injection molding materials developed for specific applications. Reaction injection molding typically utilizes epoxy aluminum complex molds, which are cost-effective and durable, capable of withstanding a high number of production cycles. The base material can be pre-colored, though cosmetic parts will often require additional painting and sanding. Reaction injection molding is ideal for creating large plastic parts with intricate details.
Structural Foam
This molding method begins with the injection of a small amount of plastic resin, followed by the use of a natural or synthetic blowing agent to expand the material within the mold. The resulting part has a closed-cell structure on the inside with a hard outer skin. During the molding process, bubbles that burst on the outer surface create a textured appearance. This effect can be corrected through sanding and painting, or by implementing other tooling enhancements. Structural foam molding is more cost-effective and generally easier to manage compared to other molding processes.
Advantages Of Low Volume Plastic Molding
- Cheaper Mold Cost: Low-volume molds are typically made from high-quality plastic, which is easier to machine and modify.
- Product to Market: This approach requires only a modest investment, allowing products to reach the market more quickly and reducing financial risk if the new product does not succeed.
- Tools: Low-volume tools can extend the product’s lifespan, especially if frequent updates are made throughout the product development cycle.
- Low Volume Merits: Often, only a few thousand parts are needed to satisfy the requirements of the entire pre-production and initial production run before transitioning to mass production.
Benefits Of Low Volume Manufacturing
Low volume manufacturing for producing low volume plastics offers several benefits:
- Cheaper: It is less costly compared to large-scale production due to lower minimum orders, which reduces tooling expenses.
- Quick Turnaround: Enjoy rapid turnaround times for mold production, allowing products to reach the market faster and providing swift access to emerging markets.
- Reduced Investment Risk: Designs can be adjusted more quickly compared to large-scale production, ensuring they are perfected before entering the market.
As a result, low volume manufacturing is becoming increasingly popular for various product types. It allows for more precise investment in manufacturing and materials, facilitates quick market entry, responds swiftly to limited product lifespans, and serves as a bridge between initial prototypes and high-volume production, especially for low volume plastic injection molding projects.
AS Prototypes’ Low Volume Plastic Injection Molding
In China, we have significant advantages in low volume manufacturing. With extensive experience in low volume production of plastic molds, we particularly excel in complex low volume plastic injection molding. Whether for simple or intricate low volume plastic molding parts, we prioritize meeting every customer’s requirements. We invite you to learn more about our manufacturing techniques in low volume injection molding to help guide your project to success.
Remain the core of our business
Whether you need micro-sized parts or larger plastic components, AS Prototypes’ extensive experience in plastic injection molding can assist you.
We are dedicated to building a more flexible and effective management team for plastic mold production, ensuring:
- Short lead times
- Quick mold changes
We are good at Types of plastic molding
Through these methods, we can help you achieve the production of complex plastic parts:
- Overmolding
- Large parts
- Insert molding
- Micro molding
We process thermoplastics
We are also working to introduce a wider variety of thermoplastics to meet the diverse needs of our global customers. Understanding your production material options for low-volume plastic parts is crucial. Here are some of the materials we offer:
- Polyetherketone (PEEK)
- High-density thermoplastics (Gravi-Tech™)
- Antimicrobial products for the food industry
- Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) materials (Fortron® or Ryton®)
- Polysulfone (PSU) materials (Udel®)
- Polyetherimide (PEI) materials (ULTEM™)
- Polyphenyl sulfone (PPSU) materials (Radel®)
- Thermally conductive plastics
For more information, please contact us at [email protected].